10 Ultimate Digital Twins Applications in Construction: Revolutionising Smart Building Performance in Africa
Digital twins applications in construction are revolutionising Africa’s building sector. By combining real-time data, simulation, and smart analytics, they are improving building performance, energy efficiency, and operational management while accelerating the continent’s smart construction transformation.
Introduction: Transforming African Construction Through Digital Twins
Africa is undergoing an infrastructure boom, with urbanisation, modern office complexes, residential developments, and transport hubs driving unprecedented construction activity. Traditional methods of monitoring and managing buildings often fall short in terms of operational efficiency, sustainability, and predictive maintenance. Enter digital twins applications in construction; virtual replicas of physical assets that capture real-time data, simulate scenarios, and empower stakeholders to make smarter, faster decisions.
By leveraging digital twin technology in construction, African developers, architects, and engineers can now track building performance, optimise energy usage, anticipate maintenance needs, and integrate advanced smart building technology in Africa. The result is a more sustainable, cost-effective, and safer infrastructure.
What Are Digital Twins in Construction?
Digital twins in construction are sophisticated virtual representations of physical buildings, infrastructure, or complex systems, designed to mirror every component and operational detail in real-time accurately. These models integrate data from sensors, IoT devices, and BIM platforms to create a living, dynamic replica of the structure. Unlike static 2D or 3D models, digital twins continuously update to reflect actual conditions on-site, capturing everything from structural health and energy consumption to occupancy patterns and equipment performance.
A digital twin captures:
- Structural performance.
- Energy behaviour.
- Water and mechanical system health.
- Environmental conditions.
- Occupancy behaviour.
In practical terms, digital twins enable construction teams, architects, and facility managers to simulate building operations, optimise systems, and predict maintenance requirements without the need for physical intervention. For instance, HVAC performance can be monitored digitally, allowing for the detection of inefficiencies before they escalate into costly repairs. Lighting, water systems, and energy consumption can all be analysed and adjusted remotely, enhancing both efficiency and sustainability.
In the African context, where infrastructure projects often face unique environmental challenges such as extreme heat, variable rainfall, or inconsistent power supplies, the use of digital twins in sustainable construction becomes even more valuable. Developers can assess how a building will perform under local climate conditions, identify potential structural vulnerabilities, and make informed decisions that extend the asset’s lifespan. Furthermore, this technology supports strategic resource allocation, reduces operational risk, and improves long-term building performance. By enabling predictive maintenance, energy optimisation, and remote monitoring, digital twins are redefining what it means to manage smart building technology efficiently in Africa.
10 Key Digital Twins Applications in Construction Reshaping Construction Across Africa
Digital twins applications in construction are rapidly transforming the way African buildings are designed, built, and operated. By combining real-time sensor data, predictive analytics, and simulation capabilities, digital twins create a living virtual mirror of physical structures. This digital representation evolves continuously based on actual site and operational conditions, giving engineers, architects, and facility managers unprecedented visibility into building behaviour.
Across fast-growing African cities, this technology is changing how infrastructure performs over its lifecycle. From hospitals and airports to office towers and universities, digital twin technology in the construction industry is enhancing decision-making, reducing operational waste, and improving asset reliability. The growing adoption of smart building technology in Africa is also accelerating the construction digital transformation Africa is experiencing, especially when digital twins are combined with BIM and digital twins integration. Below are ten major applications that demonstrate how this technology is reshaping smart building performance on the continent.
1. Real-Time Structural Health Monitoring for High-Rise Buildings
Digital twins applications in construction are rapidly changing how African cities manage the structural safety of high-rise buildings, bridges, data centres, and critical facilities. Instead of relying on periodic manual inspections, digital twin technology in construction creates a live, continuously updated virtual replica of a structure that mirrors its physical behaviour in real-time.
Advanced smart sensors embedded within concrete, steel members, and foundations continuously feed data streams into the digital twin platform. These systems track how the building responds to environmental and operational stress. This approach is particularly essential in African regions that face seismic tremors, coastal erosion, clay soils, extreme temperatures, and heavy wind loads.
These systems enable project teams to:
- Continuously monitor stress distribution across structural members.
- Track vibration frequency and amplitude during wind or traffic loads.
- Detect micro-cracking and long-term material fatigue before visible damage appears.
This form of smart building technology in Africa shifts engineers’ focus from reactive maintenance to predictive performance management. The ability to identify small structural shifts early dramatically reduces the risk of catastrophic failure while protecting asset value and human life.
Further reading: Revolutionary Smart Sensors in Concrete: 10 Key Metrics They Monitor to Improve Structural Performance
2. Energy Optimisation and Smart Building Operations
One of the most commercially valuable digital twins applications in construction is building energy performance optimisation. Digital twin technology in construction creates a real-time operational model of HVAC systems, power consumption, lighting networks, and backup energy systems.
Instead of waiting for utility bills or manual meter readings, facility teams receive live dashboards showing exactly where energy is being consumed, wasted, or overloaded. This becomes especially valuable in Africa, where rising energy tariffs and inconsistent grid supply make efficiency a strategic priority.
Key capabilities include:
- Simulating energy demand before peak usage periods.
- Automatically adjusting cooling, ventilation, and lighting patterns.
- Reducing power waste in low-occupancy zones.
- Optimising generator and battery backup performance.
The use of digital twins in sustainable construction in Africa transforms buildings into intelligent systems that actively manage operational cost and environmental impact. Smart building technology in Africa increasingly depends on real-time performance data rather than static design assumptions.
3. BIM and Digital Twins Integration for Design-to-Operation Continuity
BIM and digital twins integration represents one of the strongest foundations of construction digital transformation in Africa. BIM builds the original 3D design model, while digital twin technology in construction converts that model into a living, breathing operational asset.
Rather than leaving digital data behind at handover, the integrated model continues to evolve throughout the building lifecycle. Designers, contractors, and facility managers all work from the same unified dataset.
This integration enables:
- Seamless transfer from architects to operational teams.
- Live comparison between design intent and real-world performance.
- Faster detection of thermal, acoustic, and structural performance gaps.
- A single reliable source of truth across design, build, and operation.
Digital twins applications in construction for smart buildings in Africa increasingly depend on this integration to eliminate information silos. This eliminates disputes, improves commissioning accuracy, and creates long-term asset intelligence.
4. Predictive Maintenance for Critical Building Systems
Digital twins applications in construction have fundamentally altered maintenance strategies. Traditional maintenance models rely heavily on time-based schedules and visual inspection. Digital twin technology in construction replaces this with condition-based, predictive maintenance.
Real-time analytics continuously monitor asset health across entire systems. Components communicate their performance state before failure occurs, shifting maintenance from crisis management to planned optimisation.
Digital twin dashboards frequently monitor:
- Elevators, escalators, and vertical transport systems.
- Backup generators and electrical switchgear.
- Fire protection and suppression systems.
- Pumps, valves, and water distribution networks.
The use of digital twins in sustainable construction in Africa significantly reduces downtime, extends equipment lifespan, and lowers operational budgets. Facility managers gain stronger control over asset reliability rather than reacting to catastrophic equipment failure.
5. Smart Water Management and Leak Detection Systems
Water efficiency is no longer optional in Africa. Digital twins applications in construction allow buildings to digitally model entire plumbing and water networks in real time. Digital twin technology in water management tracks consumption, pressure, quality, and system integrity across the whole facility.
This capability is especially valuable in hospitals, hotels, manufacturing plants, and multi-storey residential towers, where wastewater can be financially and environmentally destructive.
Core system functions include:
- Continuous monitoring of flow rates and pressure levels.
- Automated leak and burst pipe detection.
- Real-time simulation of peak demand scenarios.
- Emergency shut-off automation in leak events.
This is a direct example of how digital twins are improving building performance in Africa. Smart building technology in Africa increasingly treats water as a monitored digital asset rather than a passive utility.
6. Climate-Adaptive Building Performance Simulation
Digital twins applications in construction allow African engineers to simulate how buildings respond to extreme environmental conditions. Digital twin technology in the construction of climate-adaptive structures is used both before and after construction to test real-world climate responsiveness.
Africa’s wide temperature swings, humidity exposure, dust storms, and solar heat gain require more advanced simulation tools than traditional static calculations.
This enables project teams to:
- Model solar heat gain through glazing and façade systems.
- Test passive cooling and ventilation designs.
- Simulate wind uplift, dust infiltration, and moisture penetration.
- Measure seasonal performance shifts in real time.
This capability is foundational to the future of smart construction in Africa using digital twins. Buildings are no longer designed once and forgotten. Instead, performance improves dynamically through real-world data feedback loops.
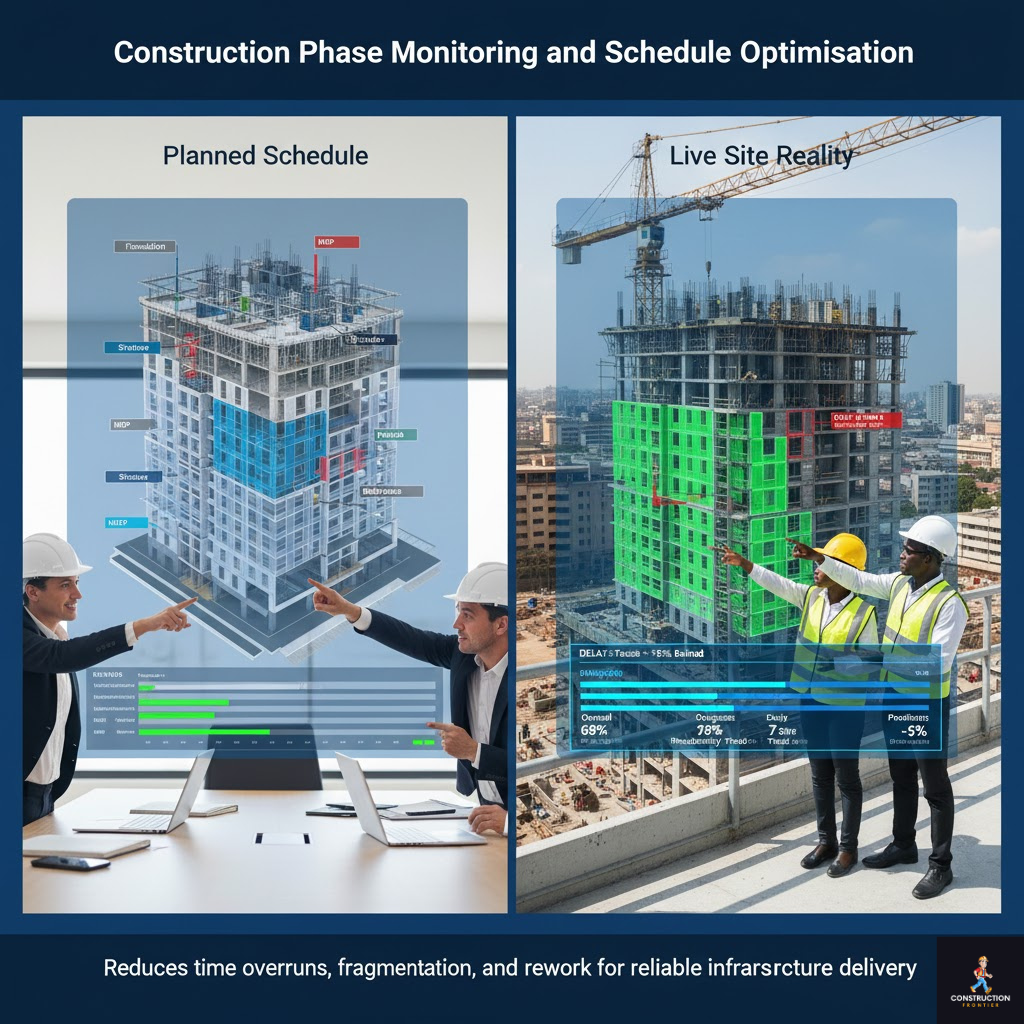
7. Construction Phase Monitoring and Schedule Optimisation
Real-world digital twin applications in African infrastructure increasingly support live construction-phase monitoring. Digital twin technology creates a live comparison between planned schedules and site reality.
Instead of waiting for weekly reports, managers view live digital progress data mapped visually to project models.
These systems support:
- Real-time progress tracking by trade and zone.
- Visual verification of installed work versus planned sequences.
- Automated delay detection and productivity trend analysis.
- Transparent reporting for clients, lenders, and regulators.
Construction digital transformation in Africa is accelerated through this capability. Digital twins applications in construction help reduce time overruns, fragmentation, and rework, creating more reliable infrastructure delivery across African markets.
8. Smart Safety Management and Risk Prediction
Digital twins applications in construction increasingly focus on human safety. Digital twin technology in construction combines environmental sensors, equipment telemetry, and worker location data to build predictive safety models.
Rather than responding after accidents occur, these systems predict risk conditions before injuries happen.
Core safety capabilities include:
- Real-time hazard zone detection.
- Automated unsafe behaviour alerts.
- Simulation of emergency evacuation workflows.
- Predictive modelling of high-risk conditions.
The use of digital twins in sustainable construction in Africa increasingly treats worker protection as a core design metric. Smart building technology in Africa now includes life-safety intelligence as part of everyday operational systems.
9. Carbon Emissions Tracking and Sustainable Building Analytics
Environmental transparency is becoming mandatory for major African developments. Digital twins applications in construction now embed carbon tracking as a built-in capability.
Digital twin technology in construction measures environmental impact across material selection, construction practices, and long-term building operation.
Systems can track:
- Embodied carbon in concrete and steel.
- Operational emissions from energy consumption.
- Waste generation and recycling efficiency.
- Lifecycle environmental performance.
The benefits of digital twin technology in African construction projects extend directly into ESG compliance, green financing eligibility, and sustainable certification frameworks. Developers gain measurable proof of sustainability rather than marketing claims.
10. Smart City Integration and Infrastructure Synchronisation
The most advanced digital twins applications in construction now connect individual buildings to city-scale digital ecosystems. Real-world digital twin applications in African infrastructure are turning buildings into intelligent urban nodes.
Instead of operating in isolation, smart buildings exchange data with public infrastructure platforms.
This integration enables:
- Live coordination with traffic management systems.
- Synchronisation with power and water grids.
- Real-time emergency system integration.
- Dynamic load balancing across urban infrastructure.
The future of smart construction in Africa, utilising digital twins, is rooted in this level of integration. Cities in Kenya, Rwanda, Morocco, Egypt, and South Africa are actively progressing toward city-scale digital twins that reshape urban planning.
Further reading: Top 10 Powerful Smart Cities Leading the Future of Urban Innovation
Benefits of Digital Twins Applications in Construction for Africa
Digital twins applications in construction deliver far more than technical convenience. They unlock strategic, operational, and financial advantages for African developers, contractors, asset owners, and public infrastructure agencies. When combined with smart building technology in Africa and BIM and digital twins integration, these systems create intelligent, self-learning structures that continuously improve how buildings perform over time.
The benefits of digital twin technology in African construction projects go beyond design. They influence decision-making, asset lifespan, operational efficiency, and long-term sustainability. As construction digital transformation in Africa accelerates, these advantages are turning digital twins from a “nice-to-have” tool into a core project requirement.
1. Higher Structural Reliability and Safety Margins
Digital twins applications in construction allow engineers to simulate real-world conditions continuously, rather than relying only on periodic inspections. Sensors embedded within concrete, steel, mechanical systems, and foundations feed live data into the digital twin, allowing engineers to monitor vibration, load stress, deflection, and fatigue.
In African infrastructure, where environmental conditions can be harsh and maintenance budgets limited, this enhanced reliability delivers major safety advantages.
Key safety improvements include:
- Early detection of micro-cracks and structural weaknesses.
- Real-time alerts for overloads and abnormal movement.
- Scenario testing for earthquakes, flooding, and extreme heat.
This directly supports digital twins applications in construction for smart buildings in Africa, where safety is not just designed but constantly measured.
2. Reduced Operational Energy and Water Costs
One of the most powerful contributions of smart building technology in Africa is its ability to reduce long-term operating costs. Digital twin technology in construction models energy flows, air movement, equipment efficiency, and water systems in real time.
Instead of responding to high bills after the fact, facility managers can:
- Optimise HVAC schedules based on real occupancy.
- Detect water leaks before they become losses.
- Adjust lighting and cooling based on environmental data.
This is one of the clearest examples of how digital twins are improving building performance in Africa by turning reactive maintenance into predictive optimisation.
3. Faster Construction Schedules and Fewer Delays
Digital twins applications in construction significantly shorten build times by reducing uncertainty and rework. When BIM and digital twins integration is used during construction, teams receive live feedback about installation errors, clashes, and sequencing issues.
This allows African contractors to:
- Detect design clashes before physical installation.
- Compare planned vs actual progress in real time.
- Simulate alternative sequences to avoid bottlenecks.
The result is fewer delays, tighter schedules, and more substantial confidence from clients and funders.
Further reading: 20 Best Construction Collaboration Software Reviewed for 2026: Top Tools for Seamless Project Management
4. Improved Transparency for Investors and Regulators
Major infrastructure developers and financiers increasingly demand transparency. Digital twins provide this through live dashboards, verified data, and visual performance models.
For African markets needing increased investor confidence, digital twins applications in construction provide:
- Trusted progress tracking.
- Verified performance benchmarks.
- Visual evidence of sustainability compliance.
This strengthens the credibility of real-world digital twin applications in African infrastructure and improves access to global funding.
5. Stronger Sustainability Performance and Reporting
Sustainability is no longer optional. Regulatory pressure and climate responsibility are forcing African developments to prove real impact.
Digital twin technology in construction enables:
- Live carbon tracking.
- Water usage optimisation.
- Material lifecycle performance analysis.
When digital twins power construction digital transformation in Africa, sustainability reporting becomes data-driven rather than estimated.
Challenges Facing Digital Twins Applications in Construction in Africa
Despite the powerful promise of digital twins applications in construction, the African market faces real-world constraints that slow adoption. These challenges are technical, financial, institutional, and cultural.
Smart building technology in Africa cannot scale without confronting these barriers directly. Understanding these obstacles is essential for contractors, consultants, and policymakers who want to drive responsible construction digital transformation in Africa.
1. High Infrastructure and Technology Costs
Digital twins applications in construction require significant upfront investment. Hardware sensors, IoT networks, cloud platforms, and specialised software packages create high entry barriers, especially for mid-sized contractors.
Typical cost pressures include:
- Embedded IoT sensor systems.
- Cloud data storage and processing.
- High-performance computing for simulations.
- Ongoing software licensing fees.
For many African infrastructure projects, budgeting for these systems competes with funding basic construction resources, slowing adoption.
2. Skills Gaps and Limited Technical Expertise
Digital twin technology in construction depends heavily on data science, software engineering, BIM expertise, and systems integration. Many African markets still face a shortage of professionals trained in:
- Data analytics and sensor data interpretation.
- BIM and digital twins integration workflows.
- Cybersecurity for connected infrastructure.
- Advanced predictive maintenance modelling.
Without strong local training pipelines, many projects rely on expensive foreign consultants, increasing costs and reducing local capacity building.
3. Connectivity and Data Reliability Issues
Digital twins rely on constant data flow. In regions where internet stability and power reliability remain challenges, real-time systems struggle to perform reliably.
Connectivity barriers include:
- Unstable broadband networks
- Power interruptions affect data continuity.
- Limited access to secure cloud infrastructure.
These gaps directly affect the effectiveness of digital twins applications in construction for smart buildings in Africa, where real-time responsiveness is critical.
4. Resistance to Digital Change
Cultural resistance remains one of the most underestimated challenges in the construction digital transformation in Africa. Many stakeholders still trust paper drawings, manual inspections, and traditional workflows.
Resistance often appears as:
- Reluctance to trust automated monitoring systems.
- Hesitation to invest in unfamiliar digital processes.
- Preference for reactive maintenance over predictive maintenance.
Until leadership embraces digital twin technology in construction at policy and organisational levels, adoption curves will remain slower than the technology allows.
Conclusion: Digital Twins as the Operating System of Africa’s Smart Buildings
Digital twins applications in construction have moved far beyond visual modelling tools. Across Africa, they are now functioning as the operating systems of next-generation buildings and infrastructure. From structural intelligence and predictive maintenance to water management, energy optimisation, carbon tracking, and city integration, the impact is measurable and accelerating.
Digital twin technology in construction, combined with BIM and digital twins integration, is redefining construction digital transformation in Africa. Projects are becoming safer, more efficient, more sustainable, and more data-driven. The future of smart construction in Africa using digital twins will not be built on guesswork. It will be driven by live data, predictive analytics, and continuously learning buildings that adapt in real time.
Call to Action: Learn More at Construction Frontier
If you want more profound insights into digital transformation, smart infrastructure, and emerging construction technologies across Africa, explore more expert content at ConstructionFrontier.com. Discover practical strategies, technical breakdowns, and industry intelligence shaping the future of construction.