Why BIM (Building Information Modelling) Matters in Africa: An Essential Guide to Smarter Construction
BIM (Building Information Modelling) is reshaping the African construction landscape. From faster project delivery to cost savings, digital construction technologies are empowering engineers, contractors, and developers across the continent to build smarter, safer, and more sustainable structures.
BIM and the Future of African Construction
Africa’s construction landscape is rapidly evolving, driven by urbanisation, infrastructure demands, and modern project requirements. The need for precision, collaboration, and data-driven decision-making increasingly challenges traditional construction methods. This is where BIM (Building Information Modelling) comes in.
BIM is more than just software; it’s a digital transformation tool that enables architects, engineers, and contractors to visualise, plan, and execute projects with unparalleled accuracy and efficiency. Across Africa, BIM adoption is accelerating, helping developers overcome challenges in cost control, scheduling, and project coordination.
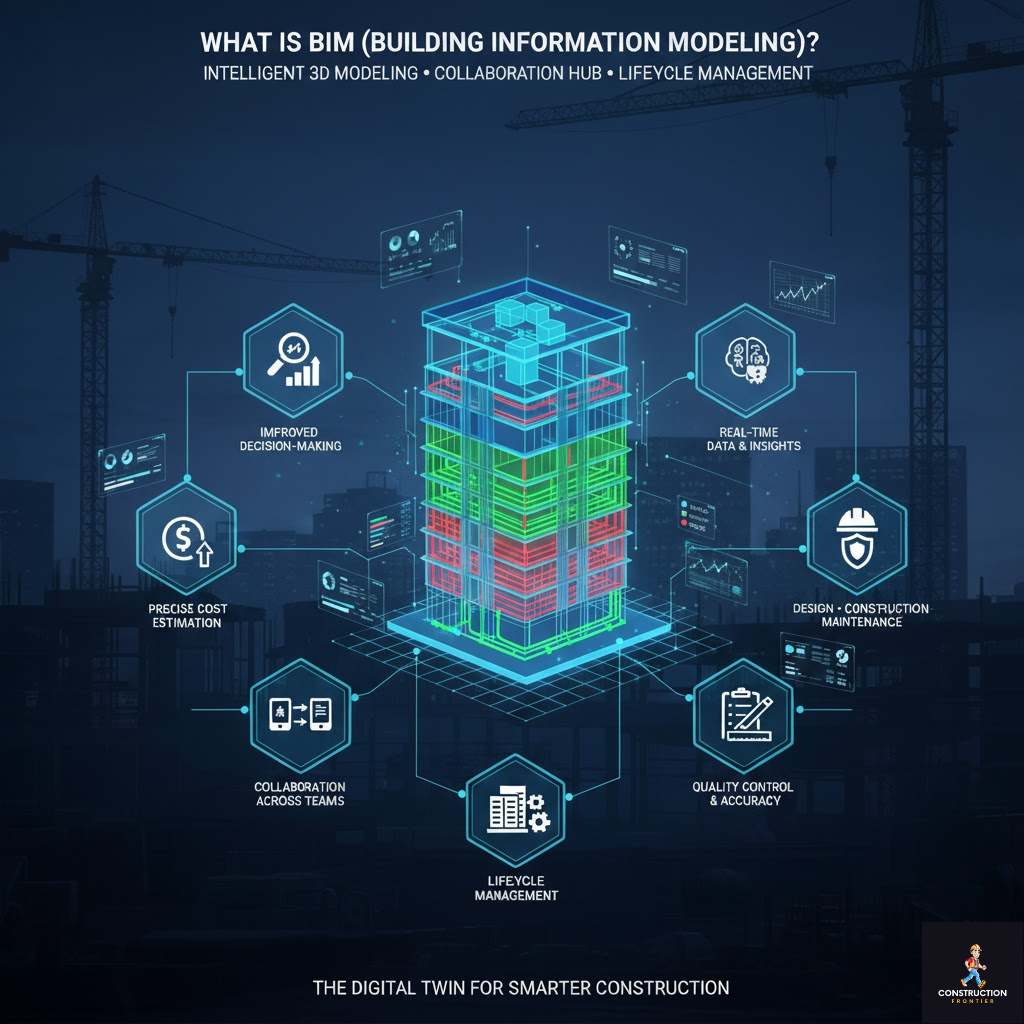
What is BIM (Building Information Modelling)?
Building Information Modelling (BIM) is a digital representation of the physical and functional characteristics of a construction project. Unlike traditional 2D drawings, BIM creates an intelligent 3D model that integrates architectural, structural, and MEP (mechanical, electrical, and plumbing) components. This model not only visualises the building but also stores critical project data, enabling real-time collaboration, precise cost estimation, and lifecycle management.
BIM acts as a centralised source of truth for all stakeholders, allowing architects, engineers, contractors, and project managers to make informed decisions. Its capabilities extend beyond design and construction, providing actionable insights for maintenance, energy efficiency, and long-term asset performance. By adopting BIM and other new construction technologies, African construction projects can reduce errors, enhance efficiency, and align with global best practices in digital construction technologies.
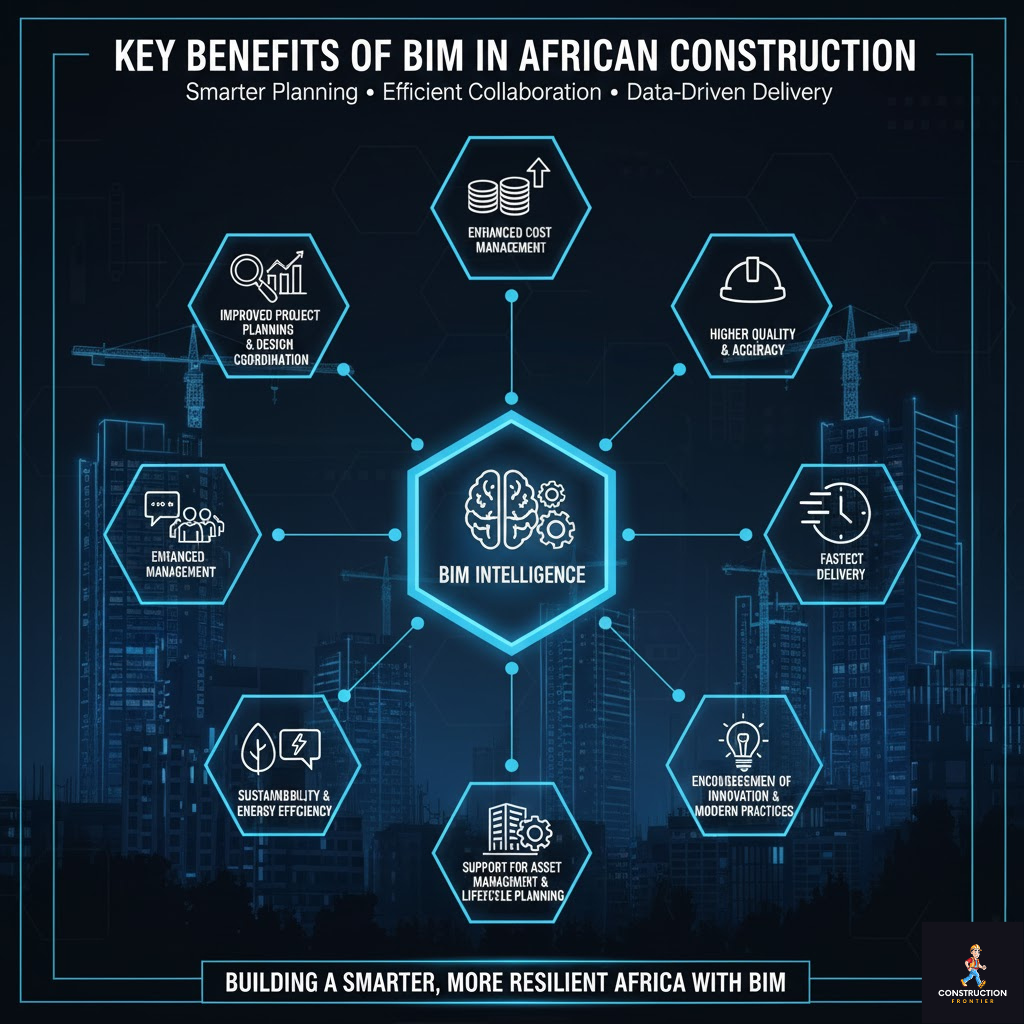
Key Benefits of BIM in African Construction
The adoption of BIM (Building Information Modelling) in Africa is transforming the construction industry by enabling smarter project planning, efficient collaboration, and data-driven decision-making. Across the continent, African engineers, architects, and contractors are leveraging BIM to reduce errors, optimise resources, and deliver projects that are both cost-effective and of high quality. Below are the most impactful benefits, fully expounded for a comprehensive understanding.
1. Improved Project Planning and Design Coordination
- BIM allows architects, engineers, and contractors to collaborate on a single digital model, identifying design conflicts early and reducing errors.
- By visualising the entire project in 3D, teams can simulate construction sequences, optimise workflows, and anticipate potential site issues before breaking ground.
- Real-life projects using BIM across Africa have reported up to a 20% reduction in design changes and reworks.
2. Enhanced Cost and Resource Management
- BIM enables precise quantity take-offs and budgeting, reducing material wastage and cost overruns.
- Resource scheduling tools within BIM models enable more effective workforce planning, equipment allocation, and supply chain management.
3. Improved Collaboration and Stakeholder Communication
- Centralised BIM models ensure all project participants, including clients and subcontractors, have access to real-time updates.
- Clash detection and project sequencing features prevent misunderstandings and facilitate smoother coordination.
- This level of transparency builds trust and reduces disputes in multi-stakeholder African projects.
4. Enhanced Risk Management
- BIM allows project teams to simulate construction sequences, identify potential hazards, and mitigate risks before they occur on-site.
- With digital clash detection, safety issues and design conflicts are flagged early, reducing accidents and costly downtime.
5. Faster Project Delivery
- The integrated workflow of BIM allows simultaneous collaboration across design, procurement, and construction stages.
- Real-time updates and automated scheduling tools streamline project timelines, helping contractors meet tight deadlines.
- African urban development projects a reduction in the effective use of BIM in the project design and construction period.
6. Higher Quality and Accuracy
- BIM’s precision in modelling ensures accurate measurements, materials specification, and construction sequencing.
- Errors from manual drafting are significantly reduced using BIM tools, resulting in higher-quality structures and fewer after-construction corrections.
- Case study: Commercial building projects undertaken by various top real estate developers across Africa have reported a reduction in rework costs of up to 18% with the integration of BIM into projects.
7. Sustainability and Energy Efficiency
- BIM integrates environmental simulations, allowing designers to assess energy performance, water usage, and carbon emissions.
- African green building initiatives have benefited from BIM by optimising designs for climate conditions and local regulations.
- By planning energy-efficient buildings digitally, developers can reduce long-term operational costs while supporting sustainable urban development.
Top Read: What is Green Building Technology? Innovative Solutions for a Sustainable Built Environment
8. Support for Asset Management and Lifecycle Planning
- BIM models can be used beyond construction for facility management, maintenance scheduling, and renovation planning.
- African infrastructure owners gain better visibility of building systems, equipment, and operational requirements.
- Long-term cost savings are realised through predictive maintenance and digital asset tracking.
9. Encouragement of Innovation and Modern Practices
- BIM facilitates the adoption of advanced construction technologies, including 3D printing, prefabrication, and modular construction.
- Contractors can prototype designs digitally, improving design creativity and accelerating innovation in African construction projects.
- Encouraging innovation positions African companies competitively on a global stage.
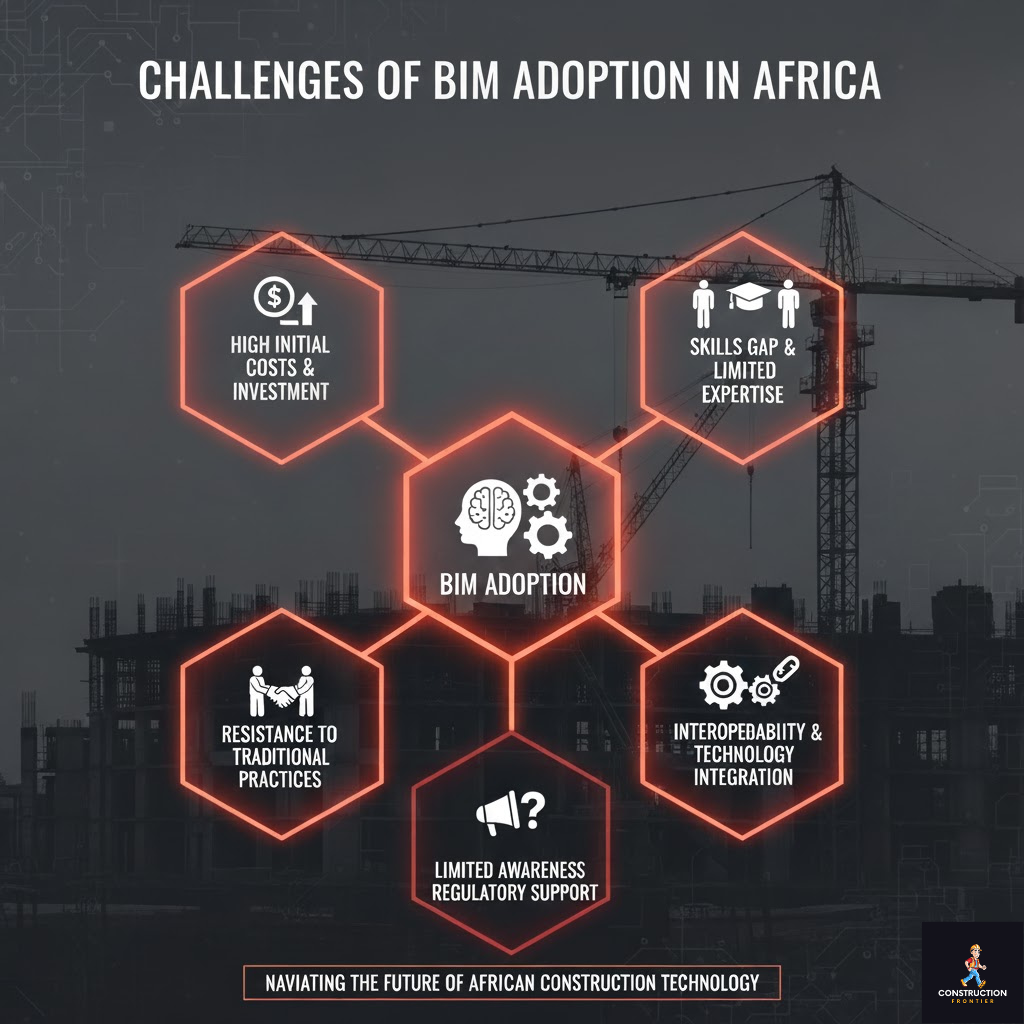
Challenges of BIM Adoption in Africa
While BIM (Building Information Modelling) promises transformative benefits for African construction projects, adoption across the continent faces several persistent challenges. These obstacles span financial, technical, cultural, and regulatory dimensions, often slowing widespread implementation despite clear advantages.
1. High Initial Costs and Investment
- Implementing BIM requires investment in software licenses, hardware, and training programs.
- Smaller contractors often struggle to afford these upfront costs, slowing adoption across the continent.
- Budget constraints in public-sector projects further complicate the rollout of BIM utilisation.
2. Skills Gap and Limited Expertise
- The shortage of skilled BIM professionals in Africa remains a major barrier.
- Training programs for architects, engineers, and construction managers are not uniform, which limits their adoption and usage.
- Companies must invest in capacity-building to ensure the proper utilisation of BIM technologies and devise ways to overcome common BIM implementation challenges.
3. Resistance to Change and Traditional Practices
- Many firms still rely on 2D drawings and conventional workflows to visualise the project outcome.
- Transitioning to digital models requires organisational culture shifts and change management strategies.
- Early adopters face challenges in convincing all stakeholders to embrace BIMs fully.
4. Interoperability and Technology Integration
- Different software platforms and incompatible file formats can hinder collaboration between teams and companies.
- African construction projects with multiple contractors may face difficulties in integrating BIM into existing systems.
- Ensuring seamless data exchange is critical for realising full BIM benefits.
5. Limited Awareness and Regulatory Support
- Some regions lack clear policies or guidelines encouraging BIM adoption.
- Without government or industry mandates, uptake remains slow in smaller markets.
- Awareness campaigns and policy frameworks are essential to foster broader implementation.
Top Read: Discover 10 Project Management Challenges Facing African Infrastructural Projects
Real-World Applications of BIM in Africa
The adoption of BIM in Africa, with organisations such as BIM Africa, is revolutionising the construction industry, enabling smarter project planning, execution, and long-term management. Integrating digital construction technologies and real-time project visualisation, BIM allows African construction teams to make informed, data-driven decisions while improving efficiency, safety, and structural performance.
1. Urban Developments
Cities like Nairobi, Lagos, and Johannesburg are leveraging BIM for high-rise buildings, urban utilities integration, and transport networks. Using 3D modelling and clash detection, planners can anticipate design conflicts, optimise space, and reduce construction delays, ensuring faster and more accurate project delivery.
2. Infrastructure Projects
Highways, railways, and bridges benefit from BIM through streamlined scheduling, resource allocation, and quality control. Projects across Kenya, Nigeria, and South Africa use BIM to prevent cost overruns, enhance site safety, and improve lifecycle management, demonstrating the practical benefits of BIM adoption in construction.
3. Commercial Buildings
Construction projects such as office towers, mixed-use developments, and hotels in Cape Town and Johannesburg rely on BIM for precise material estimation, structural optimisation, and coordinated construction workflows. This results in superior quality, reduced errors, and faster project completion.
4. Energy and Industrial Sector
Ongoing projects, such as hydropower plants and renewable energy facilities in Ethiopia and Egypt, utilise BIM for detailed engineering, structural analysis, and long-term asset management. BIM ensures operational efficiency, sustainability, and lower maintenance costs in these critical sectors.
5. Public Sector Projects
Public sector projects such as modern hospitals, schools, and governments are integrating BIM for accurate cost estimation, safety planning, and operational construction. Leveraging BIM enables African stakeholders to achieve faster project delivery, reduced costs, enhanced safety, and sustainable infrastructure outcomes.
Latest (2024–2025) BIM Case Studies & Research in Africa
Many projects in Africa have no detailed reports on the usage of specifically BIM in construction projects, but here are some of the most recent and credible BIM‑related developments, studies, and projects in Africa as of 2024–2025:
1. African BIM Report 2024
BIM Africa officially launched the African BIM Report 2024 in February 2025. Features include survey data, case studies, and insights from 32 African countries, highlighting trends in current biotech innovations, challenges, and exemplary projects. While it does not always name specific construction sites, it’s a key resource for understanding the scale and regional spread of BIM adoption in Africa.
2. Kenya – BIM Adoption Study
A paper in Acta Structilia (2025) examines BIM adoption in Kenya’s construction sector, noting that while usage is growing, coordination and information sharing remain weak. The study on the use of BIM is being utilised for design coordination, clash detection, and project information management in Kenyan firms — but many of them are still in the early stages of maturity.
3. Digital Innovation in South Africa
According to a 2024 presentation by Philangethemba Buthelezi, BIM uptake in South Africa is being driven by a push for open-collaborative BIM, everyday data environments, and standardised sharing of BIM information. The talk also emphasises diversity in BIM adoption, urging more inclusive participation from different professional backgrounds and organisations.
4. Barriers in Sub‑Saharan Africa (Modular Construction + BIM)
A 2024 study published in Buildings (MDPI) analyses the obstacles to integrating BIM in modular construction in Sub‑Saharan Africa. Key obstacles include a lack of expertise, cost, and limited standardisation, offering a realistic view of where BIM adoption still struggles in the region.
5. International Digital Tools Conference – South Africa
At the 2025 International Conference on Digital Innovation (University of Johannesburg), a study (Theme 3 and Theme 9) surveyed South African construction managers and quantity surveyors who showed interest in BIM in Africa. Interest is high but limited primarily due to cost, limited skills, and system incompatibility. This indicates that BIM is gaining awareness, but full implementation is underway for many firms.
Conclusion: Driving Smarter Construction Across Africa
BIM (Building Information Modelling) is revolutionising construction across Africa, providing a digital framework that enhances collaboration and efficiency on complex projects. By integrating architectural, structural, and MEP designs into a single 3D model, BIM allows contractors, engineers, and developers to identify design conflicts, minimise errors, and optimise project schedules. Its adoption supports cost savings, improved resource allocation, and higher-quality outcomes, which are crucial for the continent’s rapidly expanding infrastructure landscape.
Beyond efficiency, it empowers African construction professionals to adopt digital construction technologies and drive innovation. It enables real-time project tracking, better communication among stakeholders, and improved decision-making throughout the project lifecycle. By providing accurate, data-rich models, BIM enhances lifecycle management, from design and construction to operation and maintenance, ensuring sustainable and resilient infrastructure. As Africa continues to urbanise and invest in major projects, BIM adoption is becoming a critical tool for modernising the built environment and driving construction innovation across the continent.
CTA: Explore More Insights with Construction Frontier
Ready to transform your construction projects with BIM and cutting-edge digital technologies? Visit ConstructionFrontier.com for expert guides, case studies, and industry insights to stay ahead in Africa’s modern construction landscape.