AI in Civil Engineering: Powering a New Era of Innovation
AI in civil engineering is transforming how we design, build, and manage infrastructure—making projects faster, safer, and more sustainable.
A New Frontier for Civil Engineering
Civil engineering has always been a driving force behind human progress—from Roman aqueducts and medieval bridges to modern highways and skyscrapers. However, today the field faces challenges unlike any before: rapid urbanisation, climate change, rising living costs, and a demand for resilient infrastructure. To meet these pressures, the industry is turning to a powerful ally: artificial intelligence in construction and civil engineering.
AI in civil engineering is more than just automation. It enables smarter planning, predictive analytics, and data-driven decision-making that improve efficiency and sustainability. This isn’t about replacing engineers—it’s about empowering them with tools to solve increasingly complex problems.
In this article, we’ll explore AI in civil engineering, its applications, benefits, real-world examples, and the future of civil engineering and AI.
Why AI Matters in Civil Engineering
Civil engineering projects are large, complex, and expensive. Traditional approaches often face cost overruns, project delays, and safety risks. AI offers solutions by processing vast data sets, identifying risks before they escalate, and enabling engineers to design more efficiently.
According to McKinsey, global infrastructure investment needs exceed $3.7 trillion annually to keep pace with urban and economic growth. Without technological innovation, meeting this demand is nearly impossible. AI technology in infrastructure is becoming a cornerstone of sustainable and cost-effective development.
Essentially, AI doesn’t replace human expertise; it augments it, providing civil engineers with sharper insights and more accurate forecasts.
Key AI Applications in Civil Engineering
Artificial intelligence is no longer a futuristic concept in civil engineering—it is already shaping how engineers design, build, and maintain infrastructure. From highways and bridges to smart cities and mega-dams, AI-powered solutions in construction are creating efficiencies and reducing risks at every stage of a project’s lifecycle. Below are the most transformative AI applications in civil engineering.
1. Smarter Design and Planning
Every construction project begins with design, and this is where AI shines brightest. Tools like generative design algorithms can process thousands of variations of a proposed structure within minutes. Engineers input parameters such as cost constraints, material availability, safety codes, and environmental conditions. The AI then generates optimised design options that balance structural integrity, cost efficiency, and sustainability.
For example, earthquake-prone regions benefit significantly from AI-driven simulations. Instead of testing one design at a time, engineers can now model hundreds of earthquake scenarios to determine the most resilient structural configuration. These models save time and result in safer, more innovative designs.
Case Study: Some of California’s high-rise building designs use AI-powered software to ensure compliance with seismic standards and minimise material waste. This approach has reduced project costs by up to 15% compared to traditional methods.
2. Predictive Maintenance and Infrastructure Monitoring
Traditional infrastructure management is reactive—repairs happen after damage becomes visible. AI changes this by enabling predictive maintenance. Using data collected from IoT sensors, drones, and satellite imagery, AI models detect tiny anomalies, such as cracks, stress points, or rust formation, long before they develop into costly failures.
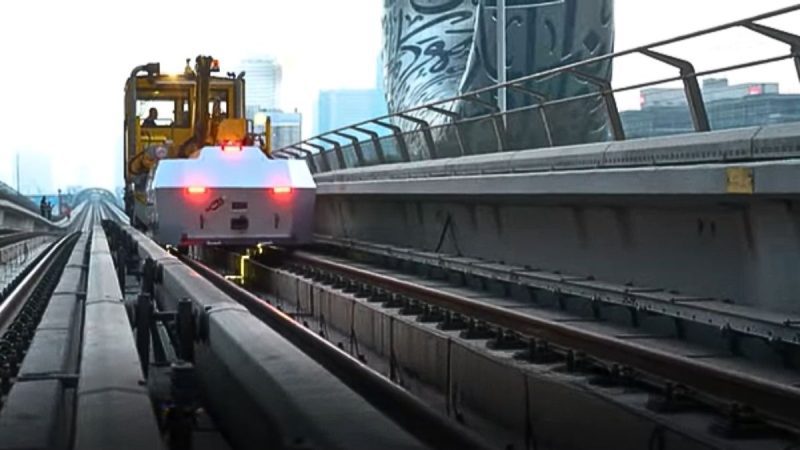
For example, railway companies are deploying AI to monitor track conditions in real time. They reduce service interruptions and enhance passenger safety by predicting when maintenance is required.
Global Insight: Japan’s use of AI-powered drones for bridge inspections has revolutionised monitoring. These drones identify invisible micro-cracks, thereby averting catastrophic failures and prolonging the lifespan of vital infrastructure.
3. Project Management and Cost Control
Civil engineering projects are notorious for budget overruns and missed deadlines. AI solves this by analysing historical project data to forecast risks, schedule delays, and resource shortages. AI-powered construction software and tools can simulate various construction timelines, recommend optimal staffing levels, and predict cost escalations in real-time. With construction margins often razor-thin, AI’s ability to improve efficiency directly impacts profitability.
Example: In Dubai, the Roads and Transport Authority (RTA) deployed an AI-powered inspection robot (ARIIS) to scan tracks and infrastructure, improving inspection speed and safety—this is a post-construction operational tool, not part of design
4. Safety Enhancements on Site
Construction sites are among the most hazardous workplaces. AI technologies now enable real-time safety monitoring through the use of cameras, wearable sensors, and predictive analytics. These systems detect unsafe behaviours, such as workers entering restricted zones without protective gear, and immediately alert supervisors.
AI-powered video analytics also identify patterns that precede accidents, allowing preventive action before incidents occur. This not only saves lives but also reduces legal and insurance costs.
Practical Use: In Singapore, contractors use AI-powered helmets that monitor worker fatigue. If fatigue indicators spike, the system issues an alert, preventing accidents caused by exhaustion.
5. Sustainable Infrastructure Development
Civil engineers face increasing pressure to deliver projects that align with sustainability and green building technology goals. AI helps by integrating climate modelling, renewable energy systems, and eco-friendly materials into project planning.
For example, AI algorithms can optimise traffic flow in urban areas, reducing congestion and emissions. Similarly, AI in construction material selection ensures the use of low-carbon concrete alternatives without compromising safety.
Case Study: In Copenhagen, AI-powered urban planning tools were used to redesign road networks for bicycles and electric vehicles. The result? A 25% drop in citywide carbon emissions within a decade. Recently, Samsung won a KSh 7.9 billion traffic system design contract to utilise AI in reducing traffic congestion in Nairobi, Kenya, with city road users expected to benefit from the initiative soon.
Benefits of AI in Civil Engineering Design and Planning
The adoption of AI in civil engineering is not just a technological upgrade—it is a game-changing shift that delivers measurable benefits. Before exploring specific advantages, it’s essential to note that AI streamlines the entire project lifecycle, from initial sketches to ongoing maintenance.
Here’s how engineers, contractors, and project owners benefit:
- Efficiency: Projects move from concept to completion faster. Optimised schedules, automated reporting, and AI-assisted modelling shorten timelines without sacrificing quality.
- Accuracy: AI minimises human error in calculations and design modelling, producing safer and more reliable infrastructure.
- Cost Savings: Smarter planning and predictive maintenance reduce the need for expensive rework, delays, and emergency repairs.
- Sustainability: AI integrates green design principles, enabling firms to meet global climate goals and secure eco-conscious tenders.
- Risk Reduction: Early problem detection means fewer accidents, lower insurance premiums, and reduced liability exposure.
According to McKinsey, firms that adopt AI in project design and planning can reduce project costs by up to 20% while increasing productivity by 30%. Therefore, as a civil engineer or a construction firm, why are you not incorporating AI techniques into your daily work?
Real-World Applications of AI in Civil Engineering Infrastructure Development
AI adoption is not confined to laboratories or tech giants; it is happening on the ground, worldwide. Civil engineering firms are deploying AI across diverse environments, proving its versatility.
- China: AI-powered tunnelling systems monitor soil conditions in real-time, reducing the risk of collapses in mega-infrastructure projects, such as high-speed rail networks.
- USA: State highway agencies are a good example of utilising AI in civil engineering to forecast road deterioration and direct maintenance budgets to areas with the most significant impact.
- Europe: Smart city initiatives utilise AI to strike a balance between rapid urban growth and sustainability, incorporating public transport, green spaces, and energy efficiency.
- Africa: As infrastructure development surges, AI-powered tools are being increasingly used for road design, bridge inspections, and cost estimation. Pilot projects in African cities, such as Nairobi, have demonstrated the ability of AI to forecast traffic congestion patterns and inform future road expansions.
These real-world applications prove that AI-powered tools for civil engineers are not futuristic—they’re essential for today’s competitiveness.
Challenges of Integrating AI in Civil Engineering
While the benefits are clear, adopting AI in civil engineering is not without obstacles. Understanding these challenges is crucial for firms planning to integrate AI into their workflows:
- High Costs: Advanced AI systems require significant upfront investment in software, hardware, and skilled personnel. Small and medium firms often struggle with affordability. Furthermore, using AI doesn’t always come cheaply. The first cost can be high, especially for smaller businesses, whether it’s for custom software, system integration, or training. Focusing on high-impact use cases that lead to early ROI is key. Automating routine jobs or making project estimates more accurate are two examples.
- Skill Gaps: Many civil engineers lack training in AI or data science, creating a learning curve that hinders the adoption of AI in civil engineering applications. They rely on interdisciplinary engineering to try to work around the missing skill sets in automation and autonomy. For adoption to be successful, people need to know both the technology and the engineering background. That means spending money on improving the skills of the people you already have on staff or hiring new people who can work with both civil engineering and data science.
- Data Quality Issues: The accuracy of AI depends on having comprehensive, high-quality data. Poorly maintained or incomplete datasets can lead to flawed predictions. Companies must ensure that the AI results they obtain align with established standards, safety regulations, and the real world. If not, automated ideas will leave you in the dark.
- Resistance to Change: Traditional firms and workers may view AI as disruptive, leading to reluctance to adopt it. The problem is both scientific and cultural in nature. Teams must understand what AI can and can’t do, as well as how it can enhance their skills. If you don’t understand that, even the strongest AI tools won’t help you.
- Legal and Ethical Considerations: Making decisions with AI raises numerous questions, particularly in safety-sensitive fields such as civil engineering. Who is in charge if something goes wrong? How do you ensure that methods are fair, explainable, and checkable? These aren’t just legal issues; they also hurt trust with customers, government officials, and the public.
- Data Privacy and Protection: AI in civil engineering relies on accurate facts and data to function effectively. However, in civil engineering, this data frequently encompasses confidential project details, proprietary models, and geospatial concepts. Before you buy an AI product, you need to know how it stores, processes, and keeps data safe. Failure to do so can be hazardous for compliance and security.
Overcoming these barriers will require government incentives, industry partnerships, and academic reforms that incorporate AI into civil engineering curricula.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in the Future of Civil Engineering
Looking forward, AI is set to redefine the profession itself. Beyond today’s applications, future innovations may reshape how infrastructure is designed, built, and managed.
- Autonomous Construction Machinery: Many construction equipment companies are heavily investing in the automation and autonomy of construction equipment and machinery. AI-driven equipment could handle excavation, bricklaying, and road paving with minimal human oversight, improving both speed and safety.
- AI-Driven Climate Adaptation Models: Engineers will use AI to simulate the effects of rising sea levels, floods, and extreme weather, ensuring resilient infrastructure. This will ensure adequate simulation design for earthquake-resistant structures such as bridges, dams, and skyscrapers.
- Digital Twins: Virtual replicas of physical infrastructure will allow engineers to test designs, monitor real-world performance, and run predictive scenarios before making costly changes. This approach will save time and costs for the overall project progress, especially during the design phase.
- Smart Cities: AI will connect transport, housing, and energy systems into unified networks that maximise efficiency and minimise waste. With the application of AI in civil engineering and transport designs, urban mobility will become more efficient, especially in emerging economies and established countries. It will allow integration with multimodal means of transport, improving commuter times and efficiency.
The future of civil engineering and AI will not replace human creativity; it will enhance it. Engineers will continue to design and innovate, but with AI as a partner that provides insights and predictions at a speed no human could match.
Final Word: Building Smarter with AI
The civil engineering profession has always adapted to new tools—from theodolites to CAD software. Today, AI in civil engineering marks a significant leap forward. Engineers who embrace AI-powered tools will deliver projects that are faster, safer, and more sustainable than ever.
Artificial intelligence in construction isn’t about replacing people; it’s about amplifying human expertise. By automating repetitive tasks, predicting risks, and generating innovative design options, AI frees engineers to focus on creativity and problem-solving.
Firms that ignore these advancements risk being left behind, while those that adopt AI technology in infrastructure will become leaders in the global green, smart, and resilient infrastructure movement.
Stay Ahead with Construction Frontier
The construction and infrastructure industries are entering a new digital era—and AI is at the centre of it. For civil engineers, contractors, and policymakers, staying informed is the first step to staying competitive.
Visit ConstructionFrontier.com for expert insights, in-depth articles, and practical strategies on how emerging technologies, such as AI, are reshaping construction and engineering worldwide.